Humanity’s pursuit of immortality has transitioned from myth and legend to a tangible scientific goal. With advancements in biotechnology, regenerative medicine, and aging research, the dream of extending human lifespans indefinitely is edging closer to reality. However, the question remains: can society sustain an immortal population? This blog explores the multifaceted challenges and implications of immortality, drawing insights from a study published on PubMed (PMID: 32449345).
Immortality would not just extend life—it would fundamentally alter society, demanding new frameworks for equality, sustainability, and purpose.
Dr. Yuval Noah Harari, Historian and Author of Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow
The Promise of Immortality
Immortality offers tantalizing possibilities: freedom from age-related decline, preservation of human knowledge, and the ability to witness centuries of progress. Innovations such as gene editing, stem cell therapy, and anti-aging drugs are already extending healthspan—the number of years lived in good health. Yet, transitioning from extended lifespans to immortality poses unprecedented societal challenges that go beyond biology.
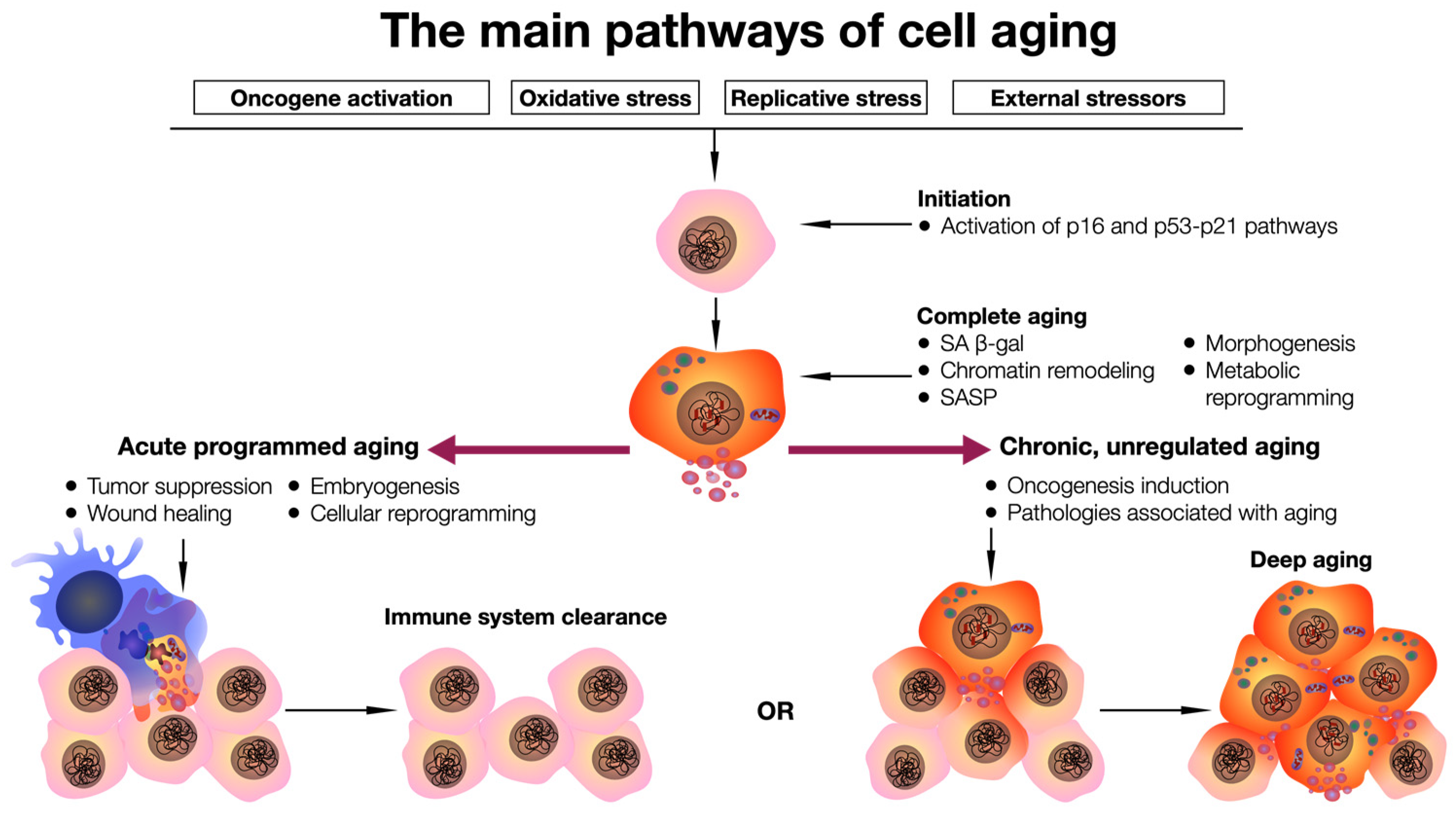
Population Dynamics and Resource Scarcity
Overpopulation: A Looming Crisis
The most immediate concern of immortality is overpopulation. If people no longer die of natural causes, the global population could grow exponentially, exacerbating resource shortages:

- Food and Water Supply: Agriculture systems, already strained by climate change, may struggle to meet the demands of a continuously expanding population.
- Housing and Urbanization: Urban centers would face overcrowding, driving up housing costs and potentially leading to sprawling, unsustainable cities.
- Healthcare Resources: While immortality might mitigate age-related diseases, managing an immortal population would require significant medical infrastructure, especially for accidents or non-aging-related illnesses.
According to projections based on existing population growth models, an immortal society would see population numbers double within decades if birth rates are not controlled. This growth would place unsustainable pressure on ecosystems, intensify deforestation, and accelerate climate change.
Economic Implications
Workforce and Employment
An immortal population would transform labor markets:
- Job Scarcity: With individuals never retiring, younger generations might struggle to find employment opportunities.
- Economic Stagnation: A static workforce could lead to stagnation in innovation and economic mobility, as older workers dominate leadership roles indefinitely.
- Pension Systems Collapse: Current retirement systems would become obsolete, necessitating entirely new economic frameworks to address perpetual employment and financial sustainability.
Wealth Inequality
Immortality technologies are likely to be expensive, at least initially, making them accessible only to the wealthy. This could create a stark divide between immortal elites and mortal masses, exacerbating existing inequalities and fueling societal unrest.
Psychological and Social Challenges
Existential and Emotional Strain
The pursuit of eternal life must not come at the cost of humanity’s moral and ecological balance.
Dr. Jane Goodall, Anthropologist and Environmentalist
Immortality may bring unforeseen psychological consequences:
- Loss of Purpose: The finite nature of life drives human ambition and creativity. Without an end, individuals may struggle with motivation or find life meaningless.
- Boredom and Mental Fatigue: Experiencing centuries of repetitive routines and relationships could lead to profound emotional exhaustion.
- Grief and Attachment: Immortals may experience prolonged grief over the loss of mortal loved ones or struggle with complex interpersonal dynamics over long timescales.
Generational Tensions
Immortality could disrupt the balance between generations:
- Cultural Stagnation: Dominance by older generations may limit cultural evolution and innovation, stifling fresh perspectives from younger individuals.
- Intergenerational Conflict: With immortality, the balance of power could shift, with younger generations resentful of older, entrenched populations holding economic and political power.
Environmental Sustainability
The study referenced (PMID: 32449345) highlights the critical link between population growth and environmental sustainability. In an immortal society:

- Carbon Emissions: A growing population of immortals would increase energy consumption, exacerbating climate change.
- Biodiversity Loss: Human expansion into natural habitats would intensify, further threatening ecosystems and species survival.
- Waste Management: Immortal populations would generate more waste over extended lifespans, posing significant challenges for sustainable waste management systems.
Addressing these issues would require innovative technologies and policies, such as renewable energy expansion, sustainable urban planning, and stringent environmental regulations.
Ethical Considerations
Access and Equity
Who gets to live forever? This question lies at the heart of the immortality debate:
- Global Disparities: Immortality technologies could widen the gap between wealthy nations and poorer ones, leading to geopolitical tensions.
- Ethical Distribution: Policymakers must grapple with whether immortality should be universal or limited to specific populations, such as individuals contributing to critical fields.
Moral Implications
Immortality challenges philosophical and ethical frameworks that have guided humanity for millennia:
- Value of Life: Does life lose its significance when it is no longer finite?
- Ethics of Population Control: Implementing measures to curb birth rates or manage immortality access raises ethical concerns about autonomy and human rights.
Potential Solutions
Population Management
To sustain an immortal society, population growth must be carefully regulated:
- Birth Control Policies: Implementing policies to control birth rates, similar to China’s former one-child policy, may become necessary.
- Artificial Habitats: Colonizing other planets or creating artificial habitats could mitigate overpopulation on Earth.
Economic Adaptations
- Flexible Retirement Systems: Redesigning retirement frameworks to account for extended lifespans and shifting career expectations.
- Universal Basic Income (UBI): Providing UBI could address job scarcity and economic inequality, ensuring basic needs are met for all.
Sustainability Innovations
Developing sustainable technologies will be critical for managing the environmental impact of an immortal population:
- Circular Economies: Transitioning to systems that prioritize recycling and minimize waste.
- Renewable Energy: Scaling renewable energy sources to reduce carbon emissions and ensure long-term sustainability.
Psychological Support Systems
Providing mental health resources tailored to the challenges of immortality could help individuals cope with its psychological effects:
- Counseling Services: Offering guidance for managing prolonged relationships, grief, and existential challenges.
- Community Building: Encouraging social networks to foster connections and combat isolation.
Final Thought: A Precarious Balance
The pursuit of immortality represents a monumental leap for humanity, promising to transform life as we know it. However, the societal, economic, and environmental challenges it poses are equally monumental. Can society sustain an immortal population? The answer depends on our ability to innovate and adapt—balancing the benefits of immortality with its profound implications.
As we stand at the brink of this new frontier, humanity must navigate the ethical and practical dilemmas with foresight, empathy, and a commitment to equity. The dream of immortality may be within reach, but sustaining it will require a collective effort to reshape the foundations of society.
Recent Insights into Can Society Sustain an Immortal Population?
“Technological Innovations to Combat Overpopulation Risks”
A 2023 study highlighted the role of AI and robotics in optimizing resource management for growing populations. Innovations in precision agriculture and renewable energy could mitigate the challenges posed by an immortal population’s demand for food and energy.
Explore the research here.
“Psychological Impacts of Eternal Life on Mental Health”
A 2022 study revealed that prolonged lifespans may lead to existential challenges such as identity crises and emotional fatigue. Enhanced mental health frameworks, including therapies designed for immortals, were shown to improve psychological resilience over centuries.
Read the full analysis here.
“Wealth Distribution Policies Address Immortality Inequalities”
In 2023, researchers analyzed the potential for progressive taxation and universal basic income (UBI) to prevent economic stagnation and wealth hoarding in an immortal society. These policies aim to balance the scales of opportunity and maintain economic vitality.
Discover more here.
“Sustainable Urban Planning for Immortal Populations”
A 2022 study explored how modular, vertically expandable cities could accommodate growing populations. These cities integrate renewable resources, circular economies, and green spaces to ensure a sustainable quality of life for immortals.
Find the details here.
“Healthcare Systems Adapt to Immortality”
A 2023 review discussed how immortality technologies would shift healthcare priorities from treating aging-related diseases to managing long-term wellness. Preventive care and advanced regenerative treatments will dominate healthcare models.
Learn more about this transformation here.
“Global Ethical Frameworks for Immortality Access”
Research published in 2022 proposed an international regulatory framework to ensure equitable access to immortality technologies. Collaborative efforts aim to prevent monopolization and promote ethical implementation worldwide.
Read the findings here.
“Environmental Innovations to Sustain Immortal Populations”
A 2023 environmental study emphasized the necessity of innovations like carbon capture and geoengineering to address the increased ecological footprint of an immortal population. Policymakers are urged to integrate these solutions into long-term sustainability plans.
Explore the research here.
“Education Reform to Support Eternal Lifespans”
In 2022, researchers suggested lifelong education systems to accommodate changing careers and societal roles in an immortal world. Continuous skill development and adaptability were identified as critical factors for maintaining economic and social progress.
Learn about these strategies here.
“AI Enhances Governance for an Immortal Society”
A 2023 study highlighted how AI-driven governance systems could optimize resource allocation, policy-making, and conflict resolution in an immortal world, ensuring fairness and efficiency in a complex global society.
Discover the potential here.
“Cultural Evolution in a World Without Death”
A 2022 sociological study explored how cultural values, traditions, and art may stagnate or transform in an immortal society. Mechanisms to preserve creativity and generational diversity are considered essential for maintaining cultural vibrancy.
Find the research here.
These insights illustrate the intricate challenges and innovative solutions needed to sustain an immortal population. Balancing longevity with societal, economic, and environmental factors will define the future of humanity.