In today’s fast-paced world, finding time for exercise can be a challenge. Yet, science continually underscores the profound benefits of physical activity on overall health and longevity. Among the different types of exercise, High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained significant attention for its potential to extend lifespan and enhance quality of life. Backed by research like the findings in a 2020 study published on PubMed, HIIT may offer unique benefits for those looking to stay youthful and vibrant as they age.
High-intensity interval training is a time-efficient strategy to get the health benefits of regular exercise in a fraction of the time.
Dr. Martin Gibala, exercise physiologist and author of The One-Minute Workout
Let’s delve into the science behind HIIT and its role in longevity.
What Is High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)?
HIIT is a form of exercise that alternates between short bursts of intense activity and brief recovery periods. For example, a typical HIIT session might involve 30 seconds of sprinting followed by 1 minute of walking, repeated for 20 minutes. This efficient workout method maximizes calorie burn and cardiovascular benefits in a fraction of the time required for traditional moderate-intensity exercise.

But beyond convenience and fitness, emerging research reveals HIIT’s potential to influence key factors that contribute to aging.
The Science Behind HIIT and Longevity
The 2020 study referenced earlier sheds light on how HIIT impacts cellular health, cardiovascular function, and metabolic processes—factors closely tied to lifespan. Here’s a breakdown of the findings:
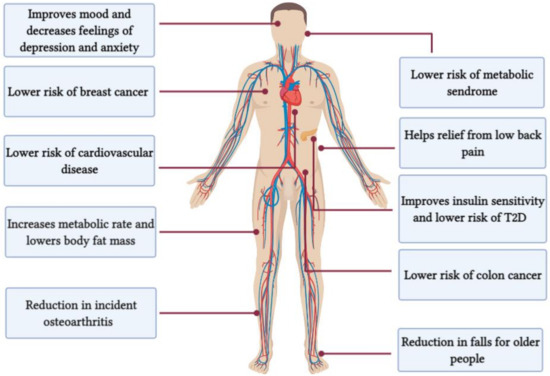
1. Improved Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, play a critical role in energy production. As we age, mitochondrial function naturally declines, contributing to reduced vitality and increased susceptibility to chronic diseases. The study found that HIIT stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, the process of generating new mitochondria, enhancing cellular energy production and resilience.
2. Reduction in Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation, often called “inflammaging,” is a significant contributor to age-related diseases. HIIT has been shown to reduce markers of systemic inflammation, helping to protect against conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s.
3. Enhanced Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally. HIIT improves heart health by increasing VO2 max (the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during exercise), reducing blood pressure, and enhancing vascular elasticity. These benefits collectively lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
4. Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Health
HIIT improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to regulate blood sugar more effectively. This can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, a condition closely linked to premature aging and shortened lifespan.
HIIT vs. Moderate-Intensity Exercise: Which Is Better?
While moderate-intensity exercise, like jogging or brisk walking, offers significant health benefits, HIIT appears to have an edge when it comes to longevity. The PubMed study found that HIIT provides comparable, if not superior, improvements in cardiovascular fitness and metabolic health in less time.
Exercise, especially high-intensity exercise, is like a drug—one of the most powerful tools we have to combat aging.
Dr. Michael Joyner, Mayo Clinic researcher on exercise and aging
Additionally, HIIT’s ability to stimulate mitochondrial function and reduce inflammation makes it particularly effective in combating the biological processes of aging. That said, both forms of exercise contribute to overall health, and the best choice often depends on individual preferences and physical capabilities.
Practical Benefits of HIIT for Longevity
- Time Efficiency: A typical HIIT workout lasts only 15–30 minutes, making it accessible even for those with busy schedules.
- Adaptability: HIIT can be tailored to different fitness levels and performed using various activities, such as running, cycling, or bodyweight exercises.
- Holistic Impact: By simultaneously improving cardiovascular, metabolic, and cellular health, HIIT addresses multiple aspects of aging in one workout.
How to Incorporate HIIT into Your Routine
Ready to add years to your life with HIIT? Here’s how to get started:

1. Choose Your Activity
HIIT can be performed using any aerobic exercise, such as cycling, running, swimming, or jumping rope. Select an activity you enjoy to increase adherence.
2. Start Small
If you’re new to HIIT, begin with a 1:2 work-to-rest ratio. For example, perform 20 seconds of intense effort followed by 40 seconds of recovery. Gradually increase intensity and reduce recovery time as you build stamina.
3. Aim for Consistency
For optimal benefits, incorporate HIIT sessions into your routine 2–3 times per week. Balance these with moderate-intensity exercise and strength training for a well-rounded fitness program.
4. Listen to Your Body
HIIT is intense by nature, so it’s important to prioritize proper form and avoid overtraining. Allow for adequate recovery between sessions to prevent injury and ensure sustainable progress.
The Caveats: Is HIIT for Everyone?
While HIIT offers numerous benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with heart conditions, joint issues, or chronic health problems should consult a healthcare professional before starting a HIIT regimen. Additionally, beginners should ease into HIIT gradually to avoid overexertion.
Real-Life Success Stories: HIIT in Action
Many individuals have experienced transformative results with HIIT, not only in terms of physical fitness but also in their overall health and vitality. For example:
- Sarah, a 45-year-old working professional, reduced her risk of diabetes and improved her energy levels by incorporating 20-minute HIIT sessions three times a week.
- John, a 60-year-old retiree, reported feeling more youthful and active after combining HIIT with his daily walks.
These stories illustrate how HIIT can make a tangible difference in enhancing both lifespan and quality of life.
The Economic Perspective: A Cost-Effective Longevity Tool
Unlike expensive anti-aging treatments or gym memberships, HIIT requires little to no equipment and can be done at home or outdoors. This makes it a highly accessible and cost-effective way to invest in your long-term health.
Final Thoughts: The Path to a Longer, Healthier Life
High-intensity exercise, particularly HIIT, holds immense promise as a tool for longevity. By enhancing mitochondrial function, reducing inflammation, and improving cardiovascular health, HIIT tackles key drivers of aging at their root. Its time efficiency and adaptability make it a practical choice for individuals of all fitness levels.
While HIIT isn’t a magic bullet, its potential to add years to your life—and life to your years—is hard to ignore. As always, consult a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program, and remember that the best exercise is the one you’ll stick with consistently.
So, why wait? Lace up your sneakers, set a timer, and start your journey toward a healthier, longer life today.
Recent Insights into High-Intensity Exercise and Longevity
“High-Intensity Exercise and Mitochondrial Resilience”
A 2024 study highlighted the ability of high-intensity exercise to enhance mitochondrial resilience by stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis and improving energy efficiency. This process supports cellular health and delays age-related decline, making high-intensity interval training (HIIT) a powerful tool for promoting longevity. The study recommends incorporating short bursts of high-intensity activity into weekly exercise routines for optimal benefits.
Read the full study here.
“Cardiovascular Longevity Through High-Intensity Exercise”
A 2023 analysis revealed that high-intensity exercise significantly boosts cardiovascular health by increasing VO2 max, improving heart rate variability, and enhancing blood vessel elasticity. These improvements collectively reduce the risk of heart disease, the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Researchers found that HIIT can deliver these benefits in a fraction of the time required for moderate-intensity exercise.
Discover the detailed findings here.
“HIIT and Inflammation Reduction”
A 2024 report examined the impact of high-intensity exercise on inflammation, showing that it reduces levels of systemic inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP). By mitigating chronic inflammation, HIIT helps combat age-related diseases, including arthritis, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders, ultimately contributing to a longer healthspan.
Learn more about the research here.
“High-Intensity Exercise and Hormetic Stress”
Research from 2023 explored how high-intensity exercise induces hormesis, a beneficial cellular stress response. This process activates protective mechanisms, including the release of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and antioxidants, which enhance cellular repair and resilience. The study highlights HIIT’s ability to strengthen the body’s defenses against aging.
Explore the study here.
“Metabolic Adaptations to High-Intensity Training”
A 2024 analysis focused on the metabolic benefits of high-intensity exercise, noting improvements in insulin sensitivity, fat oxidation, and metabolic flexibility. These adaptations reduce the risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, which are closely linked to premature aging. The research underscores the role of HIIT in enhancing overall metabolic health.
Read the full analysis here.
“Economic and Accessibility Benefits of High-Intensity Exercise”
A recent 2024 study highlighted the cost-effectiveness of high-intensity workouts, which require minimal equipment and time. Unlike expensive anti-aging treatments, HIIT provides accessible and scalable options for individuals across all socioeconomic backgrounds to improve their health and longevity.
Learn more about the findings here.
“Longevity Benefits of Short Exercise Bursts”
A 2023 report found that even short sessions of high-intensity exercise—lasting as little as 4 minutes—can significantly enhance longevity markers such as aerobic capacity and mitochondrial health. The study suggests that even the busiest individuals can benefit from brief, intense workouts integrated into daily routines.
Discover the insights here.
These recent insights showcase the profound effects high-intensity exercise can have on cellular health, cardiovascular resilience, and metabolic optimization. HIIT offers a time-efficient, accessible strategy to enhance both healthspan and lifespan. Would you like to explore any of these findings further?

























Tell more about adaptability and exercise like running, Jogging or weight exercise